Understanding movement requires grasping fundamental biomechanical principles; what is flexion represents one such essential concept. The human body, when analyzed through the lens of kinesiology, reveals flexion as a primary action occurring at joints. Consider, for example, the role of physical therapy in rehabilitating injuries that limit the normal range of flexion. Furthermore, research conducted at institutions like the National Institutes of Health (NIH) continuously expands our understanding of the physiological mechanisms underpinning flexion and its impact on overall health. Thus, comprehending what is flexion is crucial for anyone interested in health, fitness, or movement science.
Unlock Flexion: Crafting the Ideal Article Layout
This outline details the optimal structure for an article explaining flexion and its impact, prioritizing clarity and user understanding. The core keyword, "what is flexion," is central to this structure.
Defining Flexion: The Core of the Article
This section establishes the foundation. Its purpose is to answer "what is flexion" directly and comprehensively.
A Simple Explanation: What is Flexion?
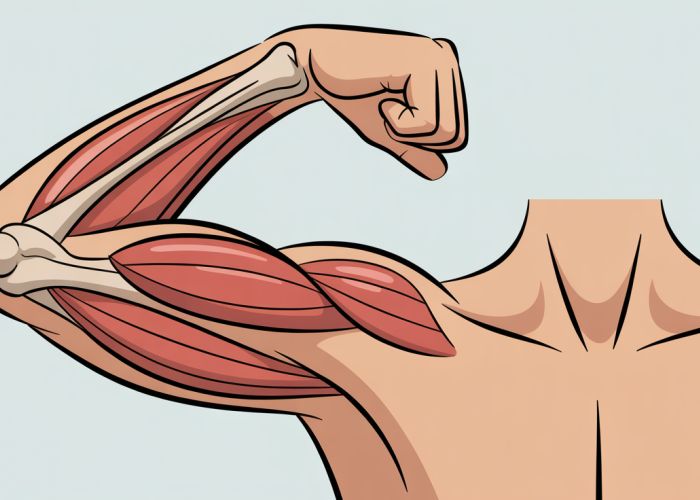
- Start with a concise definition: Flexion is the bending movement that decreases the angle between two body parts. Think of bending your elbow or knee.
- Provide visual cues: Include an introductory image or GIF illustrating flexion in different joints.
- Avoid technical jargon: Instead of "sagittal plane movement," say something like "movement forward and backward."
The Mechanics of Flexion
- Explain the role of muscles: "Flexor muscles are responsible for creating flexion. When they contract, they pull the bones closer together."
- Highlight joint involvement: Flexion occurs at joints, allowing the bones to move.
- Offer examples of different types of joints and how they flex (e.g., hinge joints like the knee, ball-and-socket joints like the hip).
Examples of Flexion in the Human Body
- Use a bulleted list to provide diverse examples:
- Bending your elbow (bringing your forearm towards your upper arm)
- Kneeling down
- Tilting your head forward
- Curling your toes
- Making a fist
Understanding the Importance of Flexion
This section shifts the focus to why flexion matters in everyday life and athletic activities.
Flexion in Daily Activities
- Show how flexion facilitates common movements.
- Use a numbered list to illustrate specific examples:
- Walking: Flexion at the hip, knee, and ankle is crucial for each step.
- Sitting: Flexion at the hips and knees allows us to sit comfortably.
- Picking up objects: Flexion at the spine (bending over) enables us to reach the ground.
- Eating: Flexion at the elbow brings food to our mouth.
- Emphasize how limitations in flexion can impede these activities.
Flexion in Exercise and Sports
- Explain how flexion contributes to athletic performance.
- Provide examples related to popular sports:
- Running: Hip flexion powers the leg drive.
- Weightlifting: Bicep curls rely entirely on elbow flexion. Squats require flexion at the hips, knees, and ankles.
- Swimming: Freestyle and breaststroke involve significant shoulder and hip flexion.
- Highlight the importance of maintaining a good range of flexion for optimal athletic function.
Limitations and Potential Problems
This section discusses potential issues related to inflexibility or excessive flexion.
Causes of Limited Flexion
- Explain factors that can restrict flexion:
- Muscle tightness or stiffness.
- Joint inflammation (arthritis).
- Injury or surgery.
- Age-related changes.
- Mention conditions that can impact flexion (e.g., hamstring strain, osteoarthritis).
The Consequences of Poor Flexion
- Describe the potential problems arising from limited flexion:
- Increased risk of injury (muscle strains, sprains).
- Compromised athletic performance.
- Difficulty performing everyday tasks.
- Increased lower back pain due to reduced hip flexion.
The Risks of Excessive Flexion (Spinal Flexion Focus)
- Specifically address the drawbacks of excessive or repetitive spinal flexion (bending forward too much).
- Use bullet points to detail the risks:
- Increased pressure on spinal discs.
- Higher risk of disc herniation.
- Potential for lower back pain and injury.
- Poor posture.
Improving and Maintaining Healthy Flexion
This section focuses on actionable advice to help readers improve their flexion.
Stretching and Exercises for Enhanced Flexion
- Recommend specific stretches for key joints:
- Hamstring stretches: For improving knee extension and hip flexion.
- Hip flexor stretches: To counter prolonged sitting.
- Shoulder stretches: To improve range of motion in the shoulders.
- Provide clear instructions and images/videos demonstrating proper form.
Lifestyle Considerations
- Offer practical tips for maintaining healthy flexion:
- Regular exercise and stretching.
- Maintaining good posture.
- Using proper lifting techniques.
- Taking breaks from prolonged sitting.
When to Seek Professional Help
- Advise readers on when to consult a doctor or physical therapist:
- If they experience persistent pain or stiffness.
- If they have difficulty performing everyday activities.
- After an injury.
- If stretches or exercises don’t alleviate their symptoms.
This structure provides a comprehensive and easily digestible explanation of flexion, its impact, and how to improve and maintain it. The focus remains on clearly answering "what is flexion" and providing actionable advice for readers.
FAQs: Understanding Flexion and Its Impact
Flexion is a fundamental movement, but understanding its nuances can be tricky. These FAQs address common questions about flexion and how it affects your body.
What exactly is flexion?
Flexion is a bending movement that decreases the angle between two body parts. Think of bending your elbow, bringing your knee towards your chest, or tilting your head forward. The opposite of flexion is extension, which increases the angle.
How does flexion affect my everyday life?
Flexion is involved in countless daily activities. From walking and sitting to lifting objects and typing on a keyboard, flexion allows us to perform these movements efficiently. Understanding proper flexion mechanics can help prevent injuries.
Why is it important to maintain a healthy range of flexion?
A good range of flexion allows for optimal movement and function. Limited flexion can restrict your ability to perform everyday tasks, potentially leading to pain, stiffness, and compensatory movements that cause further issues.
What can happen if I experience excessive or improper flexion?
Excessive or improper flexion, especially under load, can contribute to injuries. For example, repeatedly flexing your spine with poor posture while lifting can increase the risk of back pain and disc problems. Maintaining good posture and using proper lifting techniques are crucial to minimize these risks.
So there you have it – a closer look at what is flexion! Hopefully, this has shed some light on how it impacts your body. Now go move, and don’t forget to appreciate the amazing things your joints can do!