Dealing with chest pain can be unsettling, and when that pain stems from your 1st sternocostal joint, understanding the underlying issues becomes crucial. Rib cartilage, specifically at the 1st sternocostal joint, connects your rib to the sternum, and when inflamed, can lead to pain. Often, the diagnostic process involves ruling out more serious conditions such as cardiac issues, and pinpointing costochondritis as a potential culprit. Effective pain management often involves physical therapy strategies, while in some cases, specialized pain clinics can offer additional resources for 1st sternocostal joint issues.
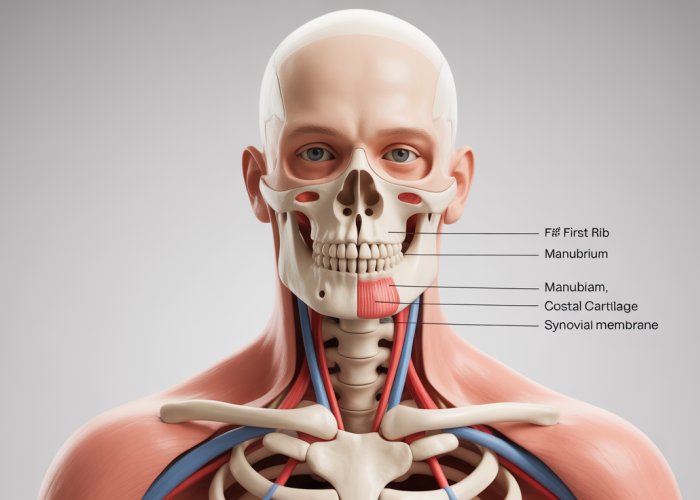
The human rib cage is a complex, yet elegant structure, crucial for respiration and protecting vital organs. A key, and often overlooked, component of this structure is the 1st sternocostal joint. This joint, connecting the first rib to the sternum, plays a significant role in the overall stability and function of the rib cage.
The Role of the 1st Sternocostal Joint
Unlike some of the other sternocostal joints, the 1st sternocostal joint has a unique, robust connection. This strong union is vital for anchoring the rib cage and facilitating the movements necessary for breathing. It allows for slight gliding and rotation, contributing to the chest’s expansion and contraction as we inhale and exhale.
Its location at the top of the rib cage makes it especially important. It helps to transmit forces throughout the entire structure during movement and respiration.
Chest Pain: A Common Complaint
Chest pain is an unfortunately common symptom that can arise from a multitude of causes, ranging from benign muscle strains to serious cardiac events. Because of this, any chest pain can be alarming and warrants careful evaluation.
However, amidst the search for the most serious causes, the 1st sternocostal joint is frequently overlooked as a potential source of discomfort.
A Frequently Overlooked Source
Pain stemming from the 1st sternocostal joint can mimic other conditions, leading to misdiagnosis and delayed treatment. Individuals may experience localized pain, tenderness, or even radiating discomfort that can easily be confused with cardiac, pulmonary, or musculoskeletal issues.
The subtle nature of the symptoms and the relative lack of awareness about this joint’s potential to cause pain contribute to its underdiagnosis.
The Importance of Accurate Diagnosis and Treatment
Given the potential for misdiagnosis, it’s crucial to consider the 1st sternocostal joint in the differential diagnosis of chest pain. A thorough physical examination, combined with a detailed medical history, is essential for identifying this often-overlooked source of discomfort.
Accurate diagnosis paves the way for appropriate treatment strategies. These might include pain management techniques, physical therapy, or other interventions aimed at alleviating pain, restoring joint function, and improving overall quality of life. Recognizing and addressing 1st sternocostal joint pain can significantly improve a patient’s well-being, offering relief from a source of chronic discomfort that might otherwise go unaddressed.
A Frequently Overlooked Source
Pain stemming from the 1st sternocostal joint can mimic other conditions, leading to misdiagnosis and delayed treatment. Individuals may experience localized pain, tenderness, or even radiating discomfort that can easily be confused with cardiac, pulmonary, or musculoskeletal issues.
The subtle nature of the joint and the vague symptoms it can produce make it a diagnostic challenge. But to fully understand why the 1st sternocostal joint can be a source of pain, we need to take a closer look at its anatomy and function within the rib cage.
Anatomy and Function of the 1st Sternocostal Joint
To appreciate the role of the 1st sternocostal joint, it’s helpful to understand what sternocostal joints are in general.
What are Sternocostal Joints?
Sternocostal joints are the articulations that connect the ribs to the sternum, or breastbone, in the anterior chest wall. These joints are crucial for the structural integrity and flexibility of the rib cage, enabling it to protect vital organs and facilitate breathing.
From the 2nd to the 7th rib, these joints are synovial, meaning they have a joint capsule and ligaments that allow for some movement. However, the 1st sternocostal joint is unique.
The Unique Anatomy of the 1st Sternocostal Joint
The 1st sternocostal joint is different from the others. It’s a cartilaginous joint, specifically a synchondrosis. This means the rib’s cartilage is directly fused to the sternum with strong fibrocartilage, creating a very firm, almost immobile connection.
This robust connection at the top of the rib cage has a very important purpose.
Relationship to the Sternum and Costal Cartilage
The 1st sternocostal joint is where the first rib meets the manubrium, the uppermost portion of the sternum. The joint is reinforced by strong ligaments that provide stability.
Unlike the other ribs, the first rib’s costal cartilage fuses directly with the sternum, forming a very stable union. This contrasts with the other sternocostal joints, which have synovial capsules allowing for more gliding movement.
The 1st Sternocostal Joint’s Role in Movement and Flexibility
While the 1st sternocostal joint has limited movement compared to the other sternocostal joints, it’s critical for overall rib cage function. Its stability provides a fixed point from which the rest of the rib cage can move during respiration.
This stable base allows the rib cage to expand and contract during breathing. Think of it as an anchor. The first rib acts as a firm foundation that helps facilitate the bucket-handle and pump-handle movements of the ribs during inhalation and exhalation.
The slight give within the cartilage of the joint also allows for the absorption of forces during physical activities. This protects the rib cage and the organs within from excessive stress.
What Causes Pain in the 1st Sternocostal Joint?
Understanding the potential causes of pain in the 1st sternocostal joint is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management. This joint, while robust, is still susceptible to various conditions that can trigger discomfort and limit functionality. Let’s delve into the primary culprits behind this often-overlooked source of chest pain.
Inflammation: The Body’s Response
Inflammation is a common underlying factor in many musculoskeletal pain conditions. It’s the body’s natural response to injury or irritation.
In the case of the 1st sternocostal joint, inflammation can arise from overuse, repetitive movements, or even underlying systemic conditions. When inflammation occurs, the surrounding tissues swell, leading to pain, tenderness, and limited range of motion.
Costochondritis: A Common Culprit
Costochondritis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the cartilage that connects the ribs to the sternum. While it can affect any of the sternocostal joints, it commonly involves the 2nd to 5th ribs. However, it can also impact the 1st sternocostal joint.
The exact cause of costochondritis is often unknown, but it can be associated with:
- Minor trauma
- Strenuous activity
- Respiratory infections
- Arthritis
It manifests as sharp, aching pain in the chest that can be reproduced by pressing on the affected joint.
Trauma and Injury to the Rib Cage
Direct trauma to the rib cage, such as from a fall, car accident, or contact sports, can directly impact the 1st sternocostal joint. These injuries can range from:
- Mild sprains
- Cartilage damage
- In more severe cases, rib fractures.
The forceful impact can disrupt the joint’s integrity, leading to inflammation, pain, and instability. Even seemingly minor injuries should be evaluated to rule out underlying damage.
Arthritis: A Degenerative Process
Arthritis, particularly osteoarthritis, is a degenerative joint disease that can affect the 1st sternocostal joint, although less commonly than other joints.
The breakdown of cartilage within the joint leads to:
- Bone-on-bone friction
- Inflammation
- Pain
This condition is more prevalent in older adults as the cartilage naturally wears down over time.
Tietze Syndrome: Swelling and Pain
Tietze syndrome is another inflammatory condition that can affect the sternocostal joints, including the 1st. Unlike costochondritis, Tietze syndrome is characterized by noticeable swelling and tenderness at the affected joint.
The cause of Tietze syndrome is often unknown, but it’s thought to be related to repetitive stress or minor trauma. The swelling and inflammation can cause significant pain and discomfort, making it difficult to perform everyday activities.
How These Causes Lead to Pain
Ultimately, all these factors – inflammation, costochondritis, trauma, arthritis, and Tietze syndrome – converge on a similar pathway: they disrupt the normal biomechanics and structural integrity of the 1st sternocostal joint.
This disruption leads to:
- Irritation of the surrounding nerves and tissues
- Triggering pain signals that are transmitted to the brain.
The pain can range from mild and achy to sharp and debilitating, significantly impacting an individual’s quality of life. Understanding the specific cause of the pain is paramount for developing an effective treatment plan that addresses the underlying issue and provides lasting relief.
Direct trauma can undoubtedly cause immediate and noticeable pain, but what about those instances where the discomfort arises seemingly out of nowhere? Recognizing the constellation of symptoms associated with 1st sternocostal joint pain is paramount for seeking timely and appropriate care. Let’s explore the key indicators that might suggest an issue with this often-overlooked joint.
Recognizing the Symptoms: What to Watch For
Identifying 1st sternocostal joint pain can be tricky, as its symptoms can mimic other conditions. However, understanding the specific characteristics of the pain and associated signs can aid in recognizing the issue.
Localized Pain: The Epicenter of Discomfort
The hallmark symptom of 1st sternocostal joint pain is, unsurprisingly, pain localized directly at the joint. This is the area where the first rib connects to the sternum, situated near the top of the breastbone, just below the collarbone.
Patients often describe the pain as sharp, achy, or even a dull throbbing sensation. The intensity can vary significantly from person to person and may fluctuate throughout the day depending on activity levels.
The pain’s consistent presence at this specific location is a key indicator that differentiates it from other potential sources of chest discomfort.
Pain Exacerbation: Movement and Breathing’s Impact
A defining characteristic of 1st sternocostal joint pain is its sensitivity to movement. Actions that involve chest expansion or upper body motion can significantly worsen the pain.
This includes:
-
Deep breathing: Taking a full, deep breath can stretch the joint and surrounding tissues, triggering or intensifying the pain.
-
Coughing or sneezing: These forceful actions put considerable stress on the rib cage and sternum, leading to sharp pain.
-
Arm and shoulder movements: Reaching, lifting, or twisting the upper body can all irritate the joint.
-
Physical activity: Exercise or strenuous activity can exacerbate the pain, especially activities involving the upper body.
Tenderness to the Touch: A Sensitive Spot
Palpation, or gentle pressing, on the 1st sternocostal joint will often reveal significant tenderness. This is a key finding during a physical examination and a reliable indicator of inflammation or irritation in the joint.
Even light pressure can elicit a sharp pain response. This localized tenderness helps to pinpoint the source of the discomfort and further differentiate it from other potential causes of chest pain.
Swelling and Redness: Signs of Inflammation
While not always present, swelling or redness around the 1st sternocostal joint can indicate inflammation. This is more common in cases of:
- Costochondritis
- Tietze syndrome
- Trauma to the area.
These visible signs of inflammation, when present, offer further evidence supporting a diagnosis of 1st sternocostal joint pain. However, it’s important to note that the absence of swelling or redness does not rule out the condition.
Radiating Pain: When Discomfort Spreads
In some instances, the pain originating from the 1st sternocostal joint can radiate to nearby areas, such as the:
- Shoulder
- Upper back
- Neck.
This radiating pain can make diagnosis more challenging, as it can mimic other musculoskeletal conditions. However, careful assessment of the primary pain location and associated symptoms can help differentiate 1st sternocostal joint pain from other sources of discomfort.
The radiating pain is often described as a dull ache or a tingling sensation, adding another layer of complexity to the patient’s experience.
Recognizing the symptoms associated with 1st sternocostal joint pain is an important first step. However, pinpointing the exact cause of chest pain necessitates a visit to a qualified healthcare professional. Let’s delve into the process of diagnosing this often-overlooked condition and what you can anticipate during a medical evaluation.
Diagnosing 1st Sternocostal Joint Pain: What to Expect
The Crucial Role of Medical Evaluation
Chest pain can be alarming, and it’s never something to self-diagnose. It’s paramount to seek the advice of a medical professional.
Prompt and accurate diagnosis is vital to rule out potentially life-threatening conditions, such as heart problems or pulmonary issues.
A healthcare provider will be able to assess your specific symptoms and medical history. They can then determine the most likely cause of your discomfort and recommend the appropriate course of action.
The Diagnostic Process Unveiled
So, what can you expect during a medical evaluation for suspected 1st sternocostal joint pain? The process typically involves a thorough assessment of your medical history, a detailed physical examination, and, in some cases, additional diagnostic testing.
Comprehensive Medical History Review
Your doctor will begin by asking detailed questions about your symptoms. These will likely cover:
- When the pain started.
- The specific location of the pain.
- What makes the pain better or worse.
- Any recent injuries or activities that might have triggered the pain.
- Your overall medical history, including any pre-existing conditions.
The Physical Examination: A Hands-On Approach
The physical examination is a critical component of the diagnostic process. Your doctor will gently palpate, or feel, the area around your sternum and ribs.
They’ll be looking for:
- Tenderness directly over the 1st sternocostal joint.
- Swelling or redness (although these are less common).
- Pain reproduction with specific movements, such as deep breathing or arm elevation.
This hands-on assessment helps the doctor pinpoint the source of the pain and differentiate it from other potential causes.
Ruling Out Other Conditions: The Role of Imaging
While a medical history and physical examination are often sufficient to diagnose 1st sternocostal joint pain. In some cases, imaging techniques may be necessary to rule out other conditions.
-
X-rays: These can help identify fractures, dislocations, or other structural abnormalities.
-
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): This can provide more detailed images of the soft tissues around the joint, helping to rule out ligament injuries or other soft-tissue problems.
-
Bone Scans: In rare cases, a bone scan may be used to detect inflammation or infection.
It’s important to note that imaging is not always necessary for diagnosing 1st sternocostal joint pain. Your doctor will determine if imaging is appropriate based on your specific symptoms and physical examination findings.
The goal of these tests isn’t necessarily to confirm 1st sternocostal joint pain, but to eliminate other, more serious potential causes of chest pain.
The absence of other identifiable causes, coupled with the symptoms and physical exam findings, often leads to a diagnosis of 1st sternocostal joint pain.
Recognizing the symptoms associated with 1st sternocostal joint pain is an important first step. However, pinpointing the exact cause of chest pain necessitates a visit to a qualified healthcare professional. Let’s delve into the process of diagnosing this often-overlooked condition and what you can anticipate during a medical evaluation.
Treatment Options for Relief
Once a diagnosis of 1st sternocostal joint pain has been confirmed and other serious conditions ruled out, the focus shifts toward effective management and relief. Thankfully, a multi-faceted approach exists, offering various avenues to alleviate discomfort and improve quality of life. From conservative strategies to more interventional techniques, the goal is to reduce pain, restore function, and prevent recurrence.
Tailoring Treatment to Individual Needs
It’s important to remember that the most effective treatment plan will vary depending on the individual, the severity of their symptoms, and any underlying contributing factors. A collaborative approach between patient and healthcare provider is essential to determine the optimal strategy.
Pain Management Strategies
At the forefront of treatment is often a focus on pain management. Several strategies can be employed, often in combination, to reduce discomfort and improve daily function.
-
Rest and Activity Modification: This involves avoiding activities that exacerbate the pain, allowing the joint to rest and heal. This doesn’t necessarily mean complete inactivity, but rather a mindful approach to movement and exertion.
-
Heat and Cold Therapy: Applying heat or cold packs to the affected area can provide temporary relief. Heat helps to relax muscles and improve blood flow, while cold can reduce inflammation and numb the area.
Anti-Inflammatory Medications (NSAIDs)
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are frequently recommended to reduce inflammation and pain associated with 1st sternocostal joint issues. These medications work by blocking the production of certain chemicals in the body that contribute to inflammation.
-
Over-the-Counter Options: Mild to moderate pain can often be managed with over-the-counter NSAIDs like ibuprofen or naproxen. It’s crucial to follow the recommended dosage and be aware of potential side effects, especially with long-term use.
-
Prescription Strength: In cases of more severe pain, a healthcare provider may prescribe stronger NSAIDs. These medications should be used under close medical supervision.
Physical Therapy: Restoring Function and Stability
Physical therapy plays a vital role in the rehabilitation process. A physical therapist can develop a customized exercise program to improve posture, flexibility, and strength in the surrounding muscles.
-
Postural Correction: Poor posture can contribute to increased stress on the sternocostal joints. Physical therapists can provide guidance on maintaining proper posture during daily activities to reduce strain.
-
Stretching Exercises: Gentle stretching exercises can help to improve flexibility in the chest and shoulder muscles, reducing stiffness and improving range of motion.
-
Strengthening Exercises: Strengthening the muscles that support the shoulder and chest can help to stabilize the rib cage and reduce stress on the 1st sternocostal joint.
Muscle Relaxants (If Prescribed)
In some instances, muscle relaxants may be prescribed to alleviate muscle spasms that contribute to chest wall pain. These medications should be used with caution and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Corticosteroid Injections (If Prescribed)
In cases of persistent and severe pain that does not respond to other treatments, corticosteroid injections may be considered. These injections involve injecting a corticosteroid medication directly into the affected joint to reduce inflammation and provide pain relief.
-
Potential Benefits: Corticosteroid injections can provide significant pain relief, allowing individuals to participate more fully in physical therapy and other rehabilitation activities.
-
Considerations: It’s important to be aware that corticosteroid injections are not a long-term solution and may have potential side effects. They are typically used as part of a comprehensive treatment plan.
Once a collaborative treatment plan is established with your healthcare provider, incorporating self-care strategies at home can significantly enhance your recovery and long-term management of 1st sternocostal joint pain. These measures empower you to take an active role in your well-being, complementing professional medical interventions and promoting sustained relief.
Home Management and Self-Care Strategies
Managing 1st sternocostal joint pain often extends beyond the clinic. Self-care strategies implemented at home play a crucial role in alleviating symptoms and promoting healing. Let’s explore some practical approaches you can adopt to manage your pain effectively.
Rest and Activity Modification
One of the first steps in managing 1st sternocostal joint pain is to provide the affected joint with adequate rest. This doesn’t necessarily mean complete bed rest, but rather a mindful approach to daily activities.
Identify and avoid activities that exacerbate your pain. This might involve modifying your exercise routine, adjusting your work habits, or simply being more conscious of your movements.
Listen to your body and take breaks when needed. Pushing through the pain can prolong recovery and potentially worsen your condition.
Posture Matters
Maintaining proper posture is paramount in reducing stress on the rib cage and supporting the healing process. Poor posture can contribute to muscle imbalances and increased strain on the 1st sternocostal joint.
Be mindful of your posture throughout the day, especially when sitting or standing for extended periods. Keep your shoulders relaxed, your back straight, and your head aligned with your spine.
Using ergonomic supports, such as lumbar cushions or adjustable chairs, can help maintain proper posture and reduce strain on the chest and back.
Gentle Stretching Exercises
Gentle stretching exercises can help improve flexibility, reduce muscle tension, and promote healing in the affected area. However, it’s crucial to approach stretching with caution and avoid any movements that cause pain.
Consulting with a physical therapist or healthcare professional can help you develop a safe and effective stretching routine tailored to your specific needs.
Some beneficial stretches might include gentle chest stretches, shoulder blade squeezes, and upper back extensions. Remember to listen to your body and stop if you experience any pain.
Heat and Cold Therapy
Applying heat or cold to the affected area can provide temporary pain relief and reduce inflammation. Heat therapy, such as warm compresses or hot showers, can help relax muscles and improve blood flow.
Cold therapy, such as ice packs, can help reduce swelling and numb pain. Experiment with both heat and cold to determine which provides the most relief for you.
Always use a barrier between your skin and the heat or cold source to prevent burns or frostbite. Apply heat or cold for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day.
Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen (Tylenol) or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) or naproxen (Aleve), can help manage pain and reduce inflammation.
Always follow the recommended dosage instructions and consult with your doctor or pharmacist if you have any questions or concerns.
Long-term use of NSAIDs can have potential side effects, so it’s essential to use them judiciously and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
While home management strategies can be incredibly beneficial, they should complement, not replace, professional medical advice. If your pain persists or worsens, it’s crucial to seek evaluation from your healthcare provider to ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Once a collaborative treatment plan is established with your healthcare provider, incorporating self-care strategies at home can significantly enhance your recovery and long-term management of 1st sternocostal joint pain. These measures empower you to take an active role in your well-being, complementing professional medical interventions and promoting sustained relief.
However, it’s equally vital to recognize when home management isn’t enough and seeking professional medical advice becomes paramount. Understanding the distinction between manageable discomfort and potentially serious underlying issues is crucial for your health and safety.
When to Seek Professional Medical Advice
While self-care strategies can provide significant relief for 1st sternocostal joint pain, there are instances where professional medical intervention is absolutely necessary. It’s important to remember that this article, like any online resource, should not replace a consultation with a qualified healthcare professional. Your health is a unique and personal matter, and a doctor or physical therapist can provide an accurate diagnosis and a tailored treatment plan.
The Importance of Professional Diagnosis
Self-diagnosing chest pain can be risky. Many conditions can mimic the symptoms of 1st sternocostal joint pain, some of which may be far more serious.
A healthcare professional can conduct a thorough physical examination, review your medical history, and order appropriate diagnostic tests (like X-rays or other imaging) to accurately determine the cause of your pain. This precise diagnosis is the foundation for effective treatment.
Consulting with a Doctor or Physical Therapist
-
Doctors: Your primary care physician can be a great first step, who can then refer you to a specialist if needed. They can assess your overall health, rule out other potential causes of chest pain (like cardiac issues), and prescribe medication if necessary.
-
Physical Therapists: A physical therapist specializes in musculoskeletal conditions. They can evaluate your posture, movement patterns, and joint mechanics to identify factors contributing to your 1st sternocostal joint pain.
They can also develop a targeted exercise program to improve flexibility, strength, and posture, thereby alleviating your symptoms.
Recognizing Red Flags: When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Certain symptoms associated with chest pain are considered "red flags," indicating a potentially life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention. Ignoring these warning signs could have severe consequences.
If you experience any of the following, seek emergency medical care immediately:
-
Severe, crushing chest pain: This type of pain, especially if accompanied by shortness of breath, sweating, nausea, or dizziness, could indicate a heart attack.
-
Sudden, sharp chest pain: Especially if accompanied by difficulty breathing, this could indicate a pulmonary embolism (a blood clot in the lungs) or other serious respiratory issues.
-
Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath: This could be a sign of a lung problem, heart problem, or other serious medical condition.
-
Pain radiating to the left arm, jaw, or back: This is another potential sign of a heart attack.
-
Loss of consciousness or fainting: This could indicate a serious underlying medical condition.
-
New or worsening chest pain in conjunction with fever, chills, or cough: This could indicate a respiratory infection like pneumonia or bronchitis.
Remember: It’s always better to err on the side of caution when it comes to chest pain. If you are unsure about the severity of your symptoms, seek immediate medical attention. Timely intervention can make all the difference. This guide is for informational purposes only and does not substitute professional medical advice.
FAQs About 1st Sternocostal Joint Pain
Here are some frequently asked questions about pain specifically affecting the 1st sternocostal joint. We hope this clarifies some common concerns.
What exactly does the 1st sternocostal joint do?
The 1st sternocostal joint connects your first rib to your sternum (breastbone). Unlike the other sternocostal joints, it’s actually a cartilaginous joint, meaning it has very limited movement. Its primary function is stability, helping to anchor the ribcage.
How is 1st sternocostal joint pain different from other chest pain?
Pain in the 1st sternocostal joint often presents as sharp, localized discomfort near the collarbone, where the first rib connects to the sternum. It may worsen with deep breaths, coughing, or specific movements of the arm and shoulder. Other chest pains may have different characteristics and locations.
What are some common causes of pain in the 1st sternocostal joint?
Common causes include trauma to the chest, overuse from activities involving the arms and shoulders, and even sleeping in an awkward position. Inflammation, known as costochondritis, can also affect the 1st sternocostal joint, causing pain.
What kind of doctor should I see for 1st sternocostal joint pain?
You can initially consult your primary care physician. They can assess your symptoms and recommend appropriate treatment or refer you to a specialist, such as a physical therapist, osteopath, or even a pain management doctor, depending on the severity and underlying cause of your 1st sternocostal joint pain.
Hopefully, this sheds some light on what might be going on with your 1st sternocostal joint and points you in the right direction for some relief. Take care of yourself!