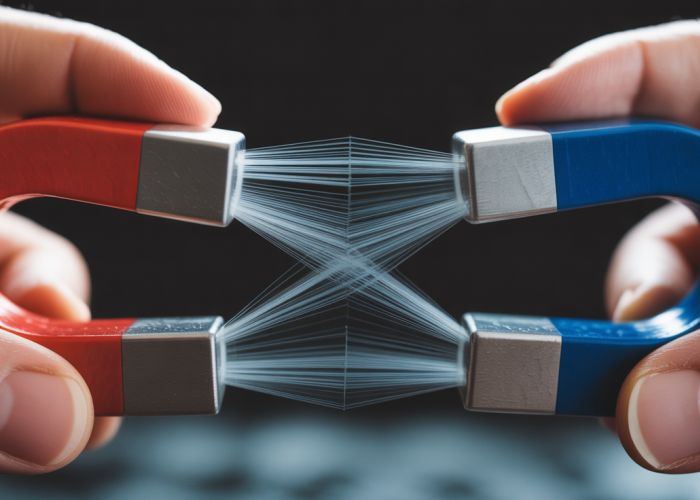
The phenomenon of magnetic repulsion force, a fundamental concept in electromagnetism, plays a crucial role in various applications. Permanent magnets exhibit this force when like poles are brought into proximity. Its understanding is vital for advancements in fields such as magnetic levitation trains, developed by organizations like the German Aerospace Center (DLR), which utilizes sophisticated calculations and computer simulations to optimize the design and efficiency of these systems. The behavior and applications of the magnetic repulsion force are further explained below.
Optimizing Article Layout for "Magnetic Repulsion Force: The Ultimate Guide!"
To create a comprehensive and reader-friendly guide on the magnetic repulsion force, a clear and structured layout is essential. This ensures the information is easily digestible and allows readers to quickly find what they’re looking for. The following breakdown provides a suggested structure, incorporating the keyword "magnetic repulsion force" naturally throughout.
Introduction: Defining Magnetic Repulsion Force
- Start with a captivating introduction that immediately explains what the magnetic repulsion force is.
- Use simple, relatable language. For example: "Have you ever tried pushing two magnets together only to feel them resist each other? That’s the magnetic repulsion force at work!"
- Briefly mention its importance and relevance in various fields.
- Incorporate the keyword "magnetic repulsion force" in the first few sentences.
- Include a visually appealing image or diagram illustrating the phenomenon.
Understanding the Fundamentals
What is Magnetism? A Prerequisite
- Briefly explain the basic concepts of magnetism.
- Describe magnetic fields and magnetic poles (North and South).
- Explain that all magnets have two poles, and that like poles repel.
- Keep this section concise as the focus is on repulsion, not magnetism in general.
The Principle of Magnetic Repulsion Force
- This is the core of the guide.
- Elaborate on how the magnetic repulsion force arises between like poles.
- Explain the interaction of magnetic fields around the magnets.
- Include diagrams illustrating the field lines and their interaction.
- Specifically state: "The magnetic repulsion force is strongest when the like poles are close together."
Factors Affecting the Strength of the Magnetic Repulsion Force
- Use a numbered list for clarity:
- Magnetic Field Strength: Stronger magnets create stronger repulsion. Describe how magnet strength is measured.
- Distance: The closer the like poles, the greater the magnetic repulsion force.
- Alignment: How the poles are aligned affects the magnitude of the force.
Mathematical Representation
Coulomb’s Law for Magnetic Forces
- Introduce the equation that describes the magnetic repulsion force.
- Explain each variable in the equation (e.g., magnetic pole strength, distance).
- Provide units of measurement for each variable.
- Use clear notation and avoid overly complex mathematical derivations.
Calculating the Magnetic Repulsion Force: Examples
- Provide several worked-out examples showing how to calculate the magnetic repulsion force in different scenarios.
- Use realistic values for magnetic pole strength and distance.
- Show the step-by-step calculations clearly.
- Include examples with varying distances to illustrate the inverse square relationship.
Real-World Applications of Magnetic Repulsion Force
Magnetic Levitation (Maglev) Trains
- Explain how the magnetic repulsion force is used to levitate trains above the tracks.
- Discuss the advantages of Maglev technology (speed, efficiency).
- Include images or diagrams of Maglev trains and their levitation systems.
Magnetic Bearings
- Describe how magnetic repulsion force is used to create frictionless bearings in machinery.
- Explain the benefits of magnetic bearings (reduced wear and tear, increased efficiency).
Other Applications
- Use a bulleted list for brevity:
- High-speed rotating equipment
- Certain types of medical equipment
- Advanced sensor technologies
Common Misconceptions about Magnetic Repulsion Force
- Address common misunderstandings about how the magnetic repulsion force works.
- For example:
- "The magnetic repulsion force only exists between permanent magnets." (Explain that it can also occur between electromagnets.)
- "The magnetic repulsion force is weaker than the magnetic attraction force." (Explain that they can be equal in magnitude but opposite in direction.)
Experimenting with Magnetic Repulsion Force (Optional)
Simple Experiments to Demonstrate Magnetic Repulsion
- Provide instructions for safe and simple experiments that readers can perform at home to experience the magnetic repulsion force firsthand.
- Examples:
- Pushing two magnets together
- Building a simple magnetic levitation device
Safety Precautions
- Emphasize the importance of safety when working with magnets, especially strong ones.
- Warn about the dangers of pinching fingers or damaging electronic devices.
FAQs About Magnetic Repulsion Force
Hopefully, this guide answered your questions about magnetic repulsion. Here are some frequently asked questions that may help clarify a few points.
What exactly causes magnetic repulsion?
Magnetic repulsion force arises from the interaction of magnetic fields. When like poles (North-North or South-South) of two magnets are brought near each other, their magnetic field lines oppose each other, creating a force that pushes them apart. This opposition is the fundamental source of magnetic repulsion force.
Is magnetic repulsion force as strong as magnetic attraction?
The strength of both magnetic repulsion force and magnetic attraction depends on several factors, including the strength of the magnets, the distance between them, and the medium in which they are interacting. However, under similar conditions, the magnitude of the magnetic repulsion force is equal to the magnitude of the magnetic attraction force.
Can I use magnetic repulsion force in practical applications?
Yes, absolutely! Magnetic repulsion force is used in various practical applications, such as maglev trains, frictionless bearings, and some types of magnetic levitation toys. The controlled application of magnetic repulsion force allows for reduced friction and innovative mechanical designs.
Does temperature affect magnetic repulsion force?
Yes, temperature can affect magnetic repulsion force. As temperature increases, the magnetic properties of some materials can weaken, leading to a decrease in the strength of their magnetic fields and therefore a reduction in the magnetic repulsion force between them.
So, that’s the gist of magnetic repulsion force! Hopefully, you now have a solid understanding. Go forth and repel (magnetically, of course)!