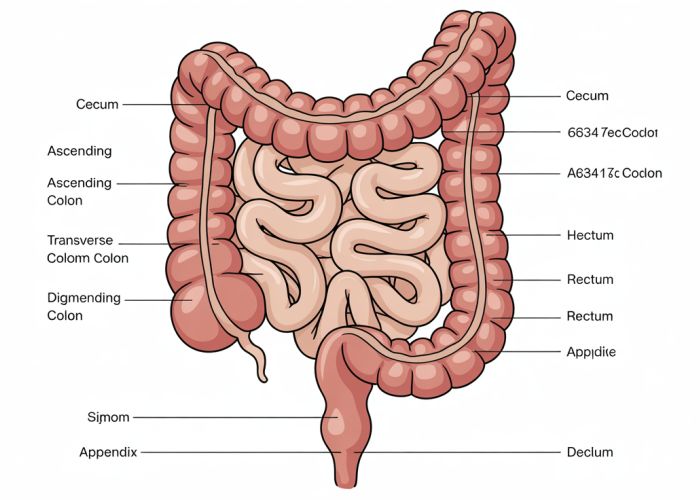
Understanding the digestive system’s intricacies is crucial for overall wellness; the large intestine, also known as the colon, plays a vital role. Gastroenterology, a specialized field of medicine, emphasizes the importance of a properly functioning large intestine for nutrient absorption and waste elimination. Examining a detailed label large intestine diagram allows medical professionals and students to correctly identify key anatomical structures such as the cecum, ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, and sigmoid colon. Furthermore, recognizing the microbiome present in the label large intestine is essential, as these microorganisms contribute significantly to digestive health and immune function. A comprehensive label large intestine examination helps to determine potential issues like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), which affects millions, requiring a carefully considered lifestyle adjustment.
Crafting the Ideal Article Layout: Label Large Intestine – Your Guide to Digestive Health!
This outline details the ideal structure for an article centered around the keyword "label large intestine," aimed at providing comprehensive information about the large intestine and its crucial role in digestive health. The layout balances detailed anatomical information with practical health advice.
I. Introduction: Setting the Stage
The introduction should immediately grab the reader’s attention and establish the importance of the large intestine.
-
Hook: Begin with a compelling statistic or a common misconception about digestion. For example: "Did you know that while most nutrient absorption happens in the small intestine, the large intestine plays a vital role in hydration and waste elimination?"
-
Define the Scope: Clearly state the article’s purpose: to provide a comprehensive understanding of the large intestine, including its structure, function, and impact on overall digestive health.
-
Keyword Integration: Naturally incorporate the keyword "label large intestine" early in the introduction, such as: "Understanding the label large intestine and each part of this vital organ is key to maintaining a healthy digestive system."
-
Outline Benefits: Briefly highlight what readers will gain from reading the article, such as:
- Identifying the different parts of the large intestine.
- Understanding the functions of each part.
- Learning how to keep their large intestine healthy.
II. Anatomy of the Large Intestine: A Labeled Tour
This section will provide a detailed anatomical breakdown of the large intestine, ensuring readers can clearly "label large intestine" components in their mind.
A. Visual Aid: The Importance of a Diagram
-
High-Quality Image/Diagram: A clear, medically accurate diagram of the large intestine is essential. This diagram should have easily identifiable and labeled parts. This directly addresses the "label large intestine" keyword. Consider including multiple views (e.g., close-up, overall digestive system).
-
Interactive Option (Optional): If possible, embed an interactive diagram that allows users to hover over or click on different sections to reveal more information.
B. Detailed Anatomical Breakdown
This part systematically describes each section of the large intestine, referencing the visual aid.
-
Cecum:
- Description of its location and shape.
- Explanation of the ileocecal valve’s function (controlling the flow from the small to the large intestine).
- Mention of the appendix and its location relative to the cecum.
-
Colon: This section should be further divided based on colon sections.
-
Ascending Colon:
- Direction of flow and location.
- Key functions in water absorption.
-
Transverse Colon:
- Description of its position across the abdomen.
- Relationship to other organs.
-
Descending Colon:
- Direction of flow and location.
- Continued water absorption.
-
Sigmoid Colon:
- S-shaped curve and its role in storing waste.
- Connection to the rectum.
-
-
Rectum:
- Description of its function as a temporary storage site for feces.
- Nerve endings and the sensation of needing to defecate.
-
Anus:
- Explanation of its structure (internal and external sphincters).
- Role in controlling bowel movements.
III. Functions of the Large Intestine: Beyond Waste
This section details the crucial functions of the large intestine.
A. Water Absorption: A Vital Role
- Explanation of how the large intestine absorbs water and electrolytes from undigested food.
- Consequences of impaired water absorption (e.g., diarrhea).
B. Bacterial Fermentation: Gut Microbiome and Health
- Discussion of the gut microbiome and its role in breaking down undigested material.
- Production of vitamins (e.g., vitamin K, B vitamins) by gut bacteria.
- Impact of gut health on overall health (e.g., immune system, mental health).
C. Waste Elimination: Forming and Storing Stool
- Explanation of how the large intestine compacts waste material into stool.
- The process of peristalsis and how it moves waste through the colon.
- The role of the rectum in storing stool until defecation.
IV. Common Large Intestine Problems and Solutions
This section provides information on common issues related to the large intestine.
A. Constipation
- Definition and common causes (e.g., dehydration, low-fiber diet, lack of exercise).
- Home remedies and lifestyle changes to relieve constipation (e.g., increasing fiber intake, drinking more water, regular exercise).
- When to seek medical advice.
B. Diarrhea
- Definition and potential causes (e.g., infections, food poisoning, medication side effects).
- Hydration strategies for managing diarrhea.
- When to seek medical advice.
C. Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
- Overview of IBS symptoms (e.g., abdominal pain, bloating, changes in bowel habits).
- Dietary and lifestyle modifications for managing IBS symptoms.
- Medical treatments for IBS.
D. Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
- Brief explanation of IBD (Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis).
- Symptoms and complications of IBD.
- Importance of medical management.
E. Colon Polyps and Cancer
- Explanation of colon polyps and their potential to become cancerous.
- The importance of regular colonoscopies for early detection and prevention of colon cancer.
- Risk factors for colon cancer.
V. Maintaining a Healthy Large Intestine: Practical Tips
This section provides actionable advice for readers.
A. Diet
- Emphasis on a high-fiber diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Limiting processed foods, sugary drinks, and red meat.
- Benefits of probiotics and prebiotics for gut health.
B. Hydration
- Importance of drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
- Avoiding excessive alcohol and caffeine, which can dehydrate the body.
C. Exercise
- Regular physical activity promotes healthy bowel movements.
- Stress reduction techniques can also benefit digestive health.
D. Regular Check-Ups
- The importance of following recommended screening guidelines for colon cancer.
- Consulting a doctor for any persistent digestive symptoms.
FAQs About Your Large Intestine and Digestive Health
Here are some frequently asked questions to help you better understand the large intestine and its role in your overall digestive health.
What is the main function of the large intestine?
The large intestine, also known as the colon, primarily absorbs water and electrolytes from undigested food. This process compacts the remaining waste material into feces, which are then stored in the rectum until elimination. Understanding how the label large intestine handles this is key to digestive health.
Where exactly is the large intestine located in the body?
The large intestine is located in the abdomen, extending from the ileum (the last part of the small intestine) to the anus. It essentially frames the small intestine. When examining a diagram that label large intestine, you will see it has ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid colon sections.
How does the large intestine differ from the small intestine?
While both are crucial for digestion, the small intestine mainly absorbs nutrients from food. The large intestine, on the other hand, primarily absorbs water and electrolytes. Also, the small intestine is longer and narrower than the label large intestine.
What are some common problems that can affect the large intestine?
Common issues include irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, colon polyps, and colon cancer. Paying attention to the health and function of your label large intestine is essential for preventing and managing these conditions.
So, there you have it! A little peek inside the fascinating world of the label large intestine. Hopefully, this helped clear things up a bit. Keep your gut happy and healthy, and remember – understanding your label large intestine is key!