Accurate cell labeling represents a critical skill in fields like cytology, where precise identification of cell components is paramount. The correct naming of structures inside the cell diagram contributes directly to a deeper understanding of cellular processes, enabling researchers and students alike to advance in biology. This guide, designed to empower you to label the cell like a pro, will show you how to take advantage of the latest techniques to master cellular anatomy.
Label the Cell Like a Pro: The Ultimate Guide for You!
This guide aims to equip you with the knowledge and skills to accurately and confidently label cell diagrams. Understanding cell structure is crucial in biology, and proper labeling is the first step toward mastery. We’ll break down the process, focusing on effective layout and clear identification of key components.
Understanding the Importance of Accurate Cell Labeling
Before we dive into the how-to, let’s quickly understand why precise labeling is so important.
- Clarity of Communication: Accurate labels prevent misinterpretations and ensure everyone understands the diagram in the same way.
- Enhanced Learning: The act of labeling reinforces your understanding of the cell’s components and their functions.
- Scientific Accuracy: Precise labels are essential for scientific presentations, reports, and publications. Inaccurate labeling can lead to flawed conclusions.
Planning Your Article Layout for "Label the Cell"
The following provides a suggested structure for your article to maximise readability and learning.
1. Introduction to Cell Structure
Begin with a brief overview of cell types (prokaryotic and eukaryotic) and the general concept of cellular organelles.
- Prokaryotic Cells: Simpler cells, like bacteria, lacking a nucleus.
- Eukaryotic Cells: More complex cells, like animal and plant cells, containing a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles.
2. Types of Cell Diagrams
Explain the different types of cell diagrams readers might encounter:
- Simplified Diagrams: These diagrams show only the essential components of a cell for easy understanding of core concepts. These are great for beginners.
- Detailed Diagrams: These provide a more comprehensive view, including more organelles and structures. More suited to higher-level study.
- 3D Renderings: While not directly "labeling", explain that 3D models provide a different perspective that can aid in understanding spatial relationships between organelles.
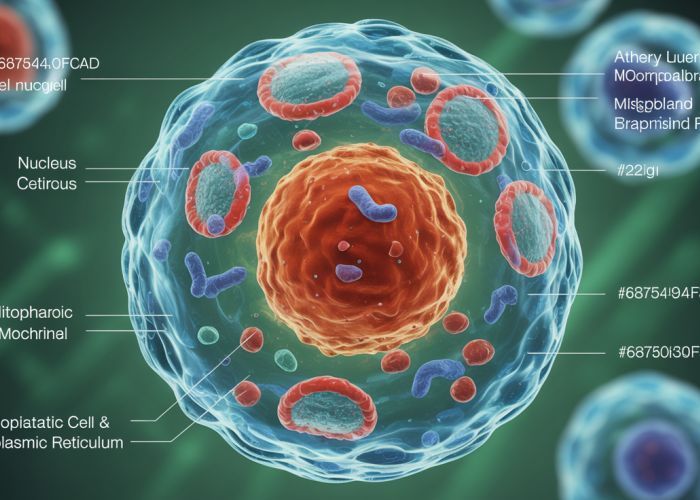
3. Key Components to Label (Focus on Common Organelles)
This section should be the core of the article, providing detailed information on each organelle. Use headings for each organelle discussed:
3.1. Cell Membrane
- Function: Describe its role in regulating what enters and exits the cell.
- Labeling Tips: Point out the importance of showing the phospholipid bilayer structure, and explaining its components (hydrophobic tails and hydrophilic heads).
3.2. Nucleus
- Function: Explain that it contains the cell’s genetic material (DNA).
- Labeling Tips: Include labels for the nuclear envelope, nucleolus, and chromatin.
3.3. Cytoplasm
- Function: Briefly explain it is the gel-like substance that fills the cell.
- Labeling Tips: Point out that it is the space around the organelles.
3.4. Mitochondria
- Function: Explain its role as the powerhouses of the cell.
- Labeling Tips: Include labels for the cristae and matrix.
3.5. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
- Function: Describe the ER’s role in protein and lipid synthesis.
- Labeling Tips: Distinguish between smooth ER (no ribosomes) and rough ER (with ribosomes).
3.6. Golgi Apparatus
- Function: Explain its role in processing and packaging proteins.
- Labeling Tips: Focus on the cis and trans faces.
3.7. Ribosomes
- Function: Explain ribosomes and their role in protein synthesis.
- Labeling Tips: Point out the free ribosomes, and the ribosomes attached to rough ER.
3.8. Lysosomes
- Function: Explain lysosomes and their role in breaking down waste.
- Labeling Tips: No specific tips are needed.
3.9. (Optional) Specific Organelles for Plant Cells
- If covering plant cells, add sections on chloroplasts (and thylakoids), cell wall, and vacuoles.
4. Tips and Tricks for Effective Labeling
Provide practical advice for creating clear and informative cell diagrams:
- Use a Ruler: Ensures straight lines for labels.
- Use Contrasting Colors: Makes labels stand out.
- Avoid Overcrowding: Space out labels for better readability.
- Label Lines Should Touch, But Not Overlap: Ensures the labels relate to a specific area of the cell, but avoid crossing lines.
- Consistency: Use consistent terminology and formatting throughout the diagram.
- Use Arrows When Necessary: Point to very specific structures.
5. Software and Tools for Digital Labeling
- Drawing Software: Mention tools like Adobe Illustrator or Inkscape for creating professional-looking diagrams.
- Image Editing Software: Discuss tools like Photoshop or GIMP for adding labels to existing images.
- Online Cell Diagram Creators: Briefly mention websites that offer pre-made cell diagrams that can be labeled online.
6. Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Mislabeling Organelles: Emphasize the importance of double-checking information.
- Incorrect Line Placement: Explain how incorrect line placement can lead to confusion.
- Illegible Handwriting: Suggest using clear, consistent fonts (if labeling digitally) or neat handwriting.
- Ignoring Scale: If showing a scaled diagram, remember to include the scale.
- Poor Colour Choices: Avoid colours that do not contrast well with the background.
FAQs: Label the Cell Like a Pro
Here are some frequently asked questions to help you master labeling cells like a pro.
Why is it important to properly label cells?
Correctly labeling cells is crucial for accurate analysis and interpretation of your data. It prevents confusion, ensures consistent formatting, and makes it easier to understand the information within the cells. Poor labeling can lead to errors and wasted time.
What are some best practices for labeling cells?
Use clear and descriptive labels. Be consistent with your terminology. Avoid abbreviations unless they are widely understood within your field. Think about how others will interpret your labels and strive for clarity when you label the cell.
How can I ensure consistency when labeling cells across a large dataset?
Consider using drop-down menus or data validation to restrict the possible values that can be entered into cells. This helps maintain uniformity and prevents inconsistencies that can arise from manual entry when you label the cell.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when labeling cells?
Avoid using special characters or excessive formatting that can interfere with data analysis. Double-check your spelling and ensure that the labels accurately reflect the data they represent. Always review your work to make sure you properly label the cell.
So, give it a shot and start labeling! With a little practice, you’ll be able to label the cell with confidence. Happy learning!