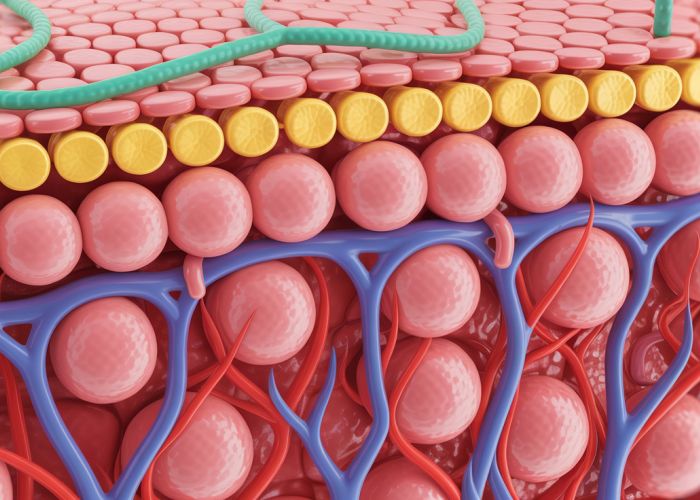
Understanding the hypodermis tissue type is crucial when studying human anatomy, as it directly impacts areas such as cosmetic surgery and the effectiveness of treatments involving subcutaneous injections. The adipose tissue within the hypodermis, for example, contributes significantly to insulation and energy storage. Researchers in the field of dermatology constantly investigate how variations in hypodermis tissue type influence skin health and overall wellbeing. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of the hypodermis tissue type, exploring its structure, function, and clinical relevance.
Structuring "Hypodermis Tissue Type: Your Ultimate Guide Revealed!" for Optimal Clarity
To create a comprehensive and engaging article on "Hypodermis Tissue Type: Your Ultimate Guide Revealed!" focusing on the keyword "hypodermis tissue type," a structured layout is essential. The following provides a detailed roadmap:
Introduction: Setting the Stage
The introduction should immediately grab the reader’s attention and clearly define the scope of the article. It should:
- Clearly state the topic: Emphasize that the article will provide a complete guide to the hypodermis tissue type. The keyword "hypodermis tissue type" should be naturally integrated here.
- Briefly define the hypodermis: Provide a concise and easy-to-understand definition of the hypodermis. What is it and where is it located?
- Highlight its importance: Explain why understanding the hypodermis is crucial. Mention its role in insulation, energy storage, and connection to underlying structures.
- Outline the article’s structure: Briefly mention the topics that will be covered in the article, such as tissue composition, functions, and related medical conditions. This helps readers understand what to expect.
Understanding the Hypodermis: A Deeper Dive
This section should delve into the specific composition and structure of the hypodermis.
The Composition of Hypodermis Tissue Type
This subsection will focus on the types of cells and components that make up the hypodermis.
- Adipocytes (Fat Cells):
- Explain what adipocytes are and their primary function in storing fat.
- Describe the arrangement of adipocytes in the hypodermis. Are they clustered or evenly distributed?
- Discuss the role of fat storage in insulation and cushioning.
- Connective Tissue:
- Identify the types of connective tissue present in the hypodermis (e.g., areolar connective tissue).
- Explain the function of connective tissue in providing support and structure.
- Detail how connective tissue fibers (collagen and elastin) contribute to the hypodermis’ elasticity.
- Blood Vessels:
- Describe the presence and function of blood vessels in the hypodermis.
- Explain how blood vessels supply nutrients and remove waste from the hypodermis and surrounding tissues.
- Nerves:
- Outline the presence and function of nerves in the hypodermis.
- Explain how nerves contribute to sensation and regulate blood flow.
The Structure of Hypodermis Tissue Type
This subsection should explain how the components of the hypodermis are organized.
- Layered Arrangement:
- Discuss whether the hypodermis is organized into distinct layers or if it’s a more uniform structure.
- If layered, describe each layer and its specific characteristics.
- Variations in Thickness:
- Explain how the thickness of the hypodermis varies in different parts of the body.
- Discuss the factors that influence hypodermis thickness, such as age, sex, and nutritional status.
Functions of the Hypodermis
This section will outline the key roles that the hypodermis plays in maintaining the body’s health.
- Insulation:
- Explain how the hypodermis helps to insulate the body and regulate temperature.
- Describe the role of fat storage in providing thermal insulation.
- Mention how the thickness of the hypodermis impacts insulation effectiveness.
- Energy Storage:
- Describe the hypodermis’s role as a major energy storage site in the body.
- Explain how stored fat can be mobilized and used for energy when needed.
- Connect this function to the body’s overall metabolism.
- Cushioning and Protection:
- Explain how the hypodermis provides cushioning and protection to underlying tissues and organs.
- Describe how the fat layer absorbs impact and reduces the risk of injury.
- Anchoring the Skin:
- Explain how the hypodermis helps to anchor the skin to underlying muscles and bones.
- Describe the role of connective tissue in providing a flexible connection.
Related Medical Conditions Affecting the Hypodermis
This section should discuss common medical conditions that can affect the hypodermis.
- Panniculitis:
- Define panniculitis and explain its causes (e.g., infection, inflammation).
- Describe the symptoms of panniculitis, such as painful nodules and inflammation.
- Outline the common treatment options for panniculitis.
- Lipomas:
- Define lipomas and explain their benign nature.
- Describe the characteristics of lipomas, such as their soft, movable texture.
- Discuss when lipoma removal may be necessary.
- Cellulite:
- Explain what cellulite is and why it occurs.
- Describe the appearance of cellulite (e.g., dimpled skin).
- Outline potential treatments for cellulite, emphasizing that results may vary.
- Lipoedema:
- Define lipoedema and explain its characteristic features of symmetrical, abnormal fat accumulation, most commonly in the legs.
- Discuss the symptoms of lipoedema, including pain and swelling.
- Outline potential treatments for lipoedema, emphasizing that it is often a progressive condition.
Maintaining a Healthy Hypodermis
This section will provide practical advice on how to keep the hypodermis healthy.
- Nutrition:
- Discuss the importance of a balanced diet for maintaining healthy fat stores.
- Highlight the role of essential fatty acids in maintaining skin health.
- Hydration:
- Explain how adequate hydration supports skin elasticity and overall hypodermis health.
- Exercise:
- Describe how regular exercise can help to maintain a healthy weight and improve blood circulation in the hypodermis.
- Sun Protection:
- Explain how excessive sun exposure can damage skin and affect the hypodermis.
- Emphasize the importance of wearing sunscreen to protect the skin.
This structured approach will allow you to craft an informative and engaging article about "hypodermis tissue type", thoroughly covering all relevant aspects while maintaining a professional and explanatory tone.
FAQs: Understanding Your Hypodermis Tissue Type
[OPENING PARAGRAPH] This FAQ section clarifies some common questions about the hypodermis tissue type and its function.
What exactly is the hypodermis?
The hypodermis is the deepest layer of your skin, located below the dermis. It’s primarily composed of adipose tissue (fat) and connective tissues. It’s also known as the subcutaneous layer.
What is the main purpose of the hypodermis tissue type?
The hypodermis serves as insulation, helping regulate body temperature. It also stores energy in the form of fat and connects the skin to underlying tissues, like muscles. The amount of hypodermis tissue type you have varies by individual.
How does the hypodermis differ from the dermis and epidermis?
The epidermis is the outermost layer of skin, primarily for protection. The dermis contains blood vessels, nerves, and hair follicles. The hypodermis, as mentioned, is mostly fat and connects the skin to deeper structures. They each have distinct compositions and functions.
Can the thickness of the hypodermis tissue type change?
Yes, the thickness of the hypodermis can change. Weight gain can increase the amount of fat stored in the hypodermis, making it thicker. Weight loss can have the opposite effect, reducing the thickness of the hypodermis tissue type.
So there you have it – your deep dive into the fascinating world of hypodermis tissue type! Hope this shed some light and made the topic a bit clearer. Now go forth and spread the knowledge… or, you know, just impress your friends with your newfound expertise on the hypodermis tissue type!