Understanding fallopian tube fertilization is crucial for many couples facing fertility challenges. In vitro fertilization (IVF) success often hinges on understanding the natural processes within the fallopian tubes. Specifically, the health of the fallopian tubes influences successful egg transport and sperm viability; issues here can sometimes be addressed through microsurgical techniques championed by centers like the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM). Effective treatments, including those involving improved ovarian stimulation protocols, are vital to optimize fertilization rates.
Maximizing Your Chances with Fallopian Tube Fertilization
Understanding fallopian tube fertilization is crucial when you’re trying to conceive. This article layout focuses on providing you with information that’s both helpful and supportive, empowering you to explore all available options. The central keyword, "fallopian tube fertilization," will be naturally integrated throughout the text, ensuring clarity and relevance.
Understanding Fallopian Tube Function and Fertilization
This section lays the groundwork by explaining the role of the fallopian tubes in natural conception. We’ll focus on making complex biological processes easy to understand.
The Fallopian Tubes: Your Natural Conception Pathways
- Anatomy and Function: Briefly describe the structure of the fallopian tubes (fimbriae, ampulla, isthmus, intramural portion) and their role in capturing the egg released from the ovary.
- Egg Transport: Explain how the egg is moved through the tube towards the uterus. Mention the importance of cilia lining the tubes.
- Sperm Transport: How sperm travel from the uterus, through the tubes, towards the egg. Highlight the challenges sperm face.
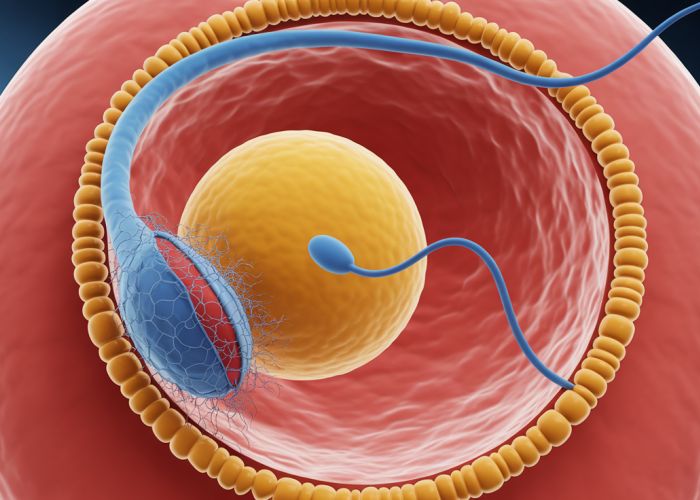
- Fertilization Site: Emphasize that fertilization typically occurs in the ampulla of the fallopian tube.
The Fertilization Process: A Step-by-Step Overview
- Sperm Arrival: Describe the arrival of sperm at the egg, after navigating the female reproductive tract.
- Penetration: Explain how the sperm penetrates the outer layers of the egg.
- Genetic Fusion: Detail the fusion of the sperm and egg genetic material, resulting in a zygote.
- Zygote Transport: Explain how the newly formed zygote begins its journey down the fallopian tube to the uterus.
Factors Affecting Fallopian Tube Fertilization
This section dives into the problems that can hinder fertilization. We’ll address the common issues and their impact.
Fallopian Tube Blockage: A Significant Barrier
- Causes of Blockage:
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): Detail how PID, often caused by STIs, can lead to scarring and blockage.
- Endometriosis: Explain how endometrial tissue outside the uterus can affect fallopian tube function.
- Previous Ectopic Pregnancy: How a previous ectopic pregnancy can damage the tube.
- Surgery: Discuss how prior abdominal or pelvic surgery can potentially lead to adhesions and blockage.
- Diagnosis: Describe how fallopian tube patency is assessed (e.g., hysterosalpingogram (HSG), laparoscopy with dye).
- Symptoms: Although not always present, describe potential symptoms like pelvic pain or infertility.
Other Conditions Affecting Fallopian Tube Fertilization
- Fallopian Tube Damage: Explain that even without complete blockage, damage to the fallopian tubes can hinder fertilization.
- Hydrosalpinx: Briefly explain how fluid buildup in the tubes can prevent fertilization and implantation.
- Cilia Damage: Detail how damage to the cilia lining the tubes can impede egg transport.
- Age-Related Decline: Discuss the age-related decline in egg quality and its impact on successful fertilization in the fallopian tubes.
Boosting Your Chances: Strategies to Enhance Fallopian Tube Fertilization
This is the core section, offering practical advice and potential solutions.
Medical Interventions: Exploring Your Options
- Fallopian Tube Surgery:
- Laparoscopy: Explain how laparoscopy can be used to remove adhesions or open blocked tubes. Be realistic about success rates.
- Salpingectomy: Explain the option of removing a damaged fallopian tube, particularly in cases of hydrosalpinx, before IVF.
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF):
- IVF as an Alternative: Explain how IVF bypasses the fallopian tubes entirely, offering a solution for those with blocked or damaged tubes. Clearly state that fertilization happens outside of the body in this procedure.
- When IVF is Recommended: Describe situations where IVF is a more appropriate option than surgery (e.g., severe tube damage, advanced maternal age).
Lifestyle Modifications: Supporting Natural Fertility
- Healthy Diet: Suggest a balanced diet rich in nutrients important for reproductive health.
- Antioxidants: Highlighting foods rich in antioxidants and their role in reproductive health.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Mentioning the potential benefits of omega-3 fatty acids.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Explain the impact of being overweight or underweight on fertility.
- Quit Smoking: Emphasize the negative impact of smoking on egg quality, sperm quality, and overall reproductive health.
- Limit Alcohol and Caffeine: Provide recommendations for alcohol and caffeine consumption.
- Stress Management: Suggest relaxation techniques like yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature.
- Timing Intercourse: Describe the importance of timing intercourse around ovulation for optimal chances of fertilization. Using ovulation predictor kits.
- Supplements: Briefly mention supplements that may be beneficial (e.g., folic acid, CoQ10), but always advise consulting with a healthcare professional before taking any new supplements.
Natural Remedies: A Complementary Approach (Use Cautiously)
- Herbal Remedies: Disclaimer: This section should be approached with caution. Emphasize the importance of discussing any herbal remedies with a healthcare provider. Provide brief information on some herbs that some practitioners suggest may be helpful for fertility. Mention potential side effects and interactions.
- Acupuncture: Discuss acupuncture as a complementary therapy that may help improve blood flow to the reproductive organs. Refer to research studies (if possible).
Seeking Professional Guidance
This section stresses the importance of consulting with fertility specialists.
When to Consult a Fertility Specialist
- Age: Recommend seeking help sooner rather than later, especially for women over 35.
- History of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): If there’s a history of PID, emphasize the need for evaluation.
- Irregular Periods: Highlight irregular menstrual cycles as a sign of potential underlying fertility issues.
- Previous Ectopic Pregnancy: Emphasize the need for evaluation after an ectopic pregnancy.
- Unsuccessful Conception Attempts: Recommending a consultation after 12 months of trying to conceive (or 6 months if the woman is over 35).
What to Expect During a Fertility Evaluation
- Medical History: Discuss the importance of providing a detailed medical history to the fertility specialist.
- Physical Examination: Explain that a physical examination will be part of the evaluation.
- Diagnostic Tests: Describe common diagnostic tests, such as blood tests (hormone levels), ultrasound, and HSG.
- Personalized Treatment Plan: Emphasize that the fertility specialist will develop a personalized treatment plan based on the individual’s specific needs and circumstances.
Fallopian Tube Fertilization: FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about fallopian tube fertilization and how you can potentially improve your chances of conception.
What exactly is fallopian tube fertilization?
Fallopian tube fertilization is the natural process where a sperm cell meets and fertilizes an egg inside one of the fallopian tubes. This fertilized egg then travels to the uterus for implantation. Successful fertilization here is crucial for natural pregnancy.
What factors can affect fallopian tube fertilization?
Several factors can hinder this process, including blocked or damaged fallopian tubes, endometriosis, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), and age-related decline in egg quality. These conditions can physically prevent sperm from reaching the egg or impair the tube’s ability to support fertilization.
Are there ways to improve my chances of fallopian tube fertilization?
Yes, maintaining a healthy lifestyle is key. This includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. Managing stress is also important, as high stress levels can impact hormonal balance and fertility.
If natural fallopian tube fertilization is unsuccessful, what are my other options?
If natural attempts are unsuccessful, assisted reproductive technologies (ART) such as In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) offer alternative pathways to pregnancy. IVF bypasses the fallopian tubes completely, as fertilization occurs outside the body, and the resulting embryo is then transferred directly to the uterus.
So, whether you’re just starting to research or exploring different options, remember that understanding **fallopian tube fertilization** is a key piece of the puzzle. Take things one step at a time, and we’re rooting for you!